What is Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback therapy is a treatment method that uses a sound-based biofeedback technology to help retrain the brain to self-regulate and function optimally. This computer-based program, which began in the 1950s as part of NASA's training program for astronauts, uses sound or visual signals to retrain or reorganize the brain signals. By responding to this process, the client then learns to regulate and improve their brain function and alleviate the symptoms related to various neurological and mental health disorders.
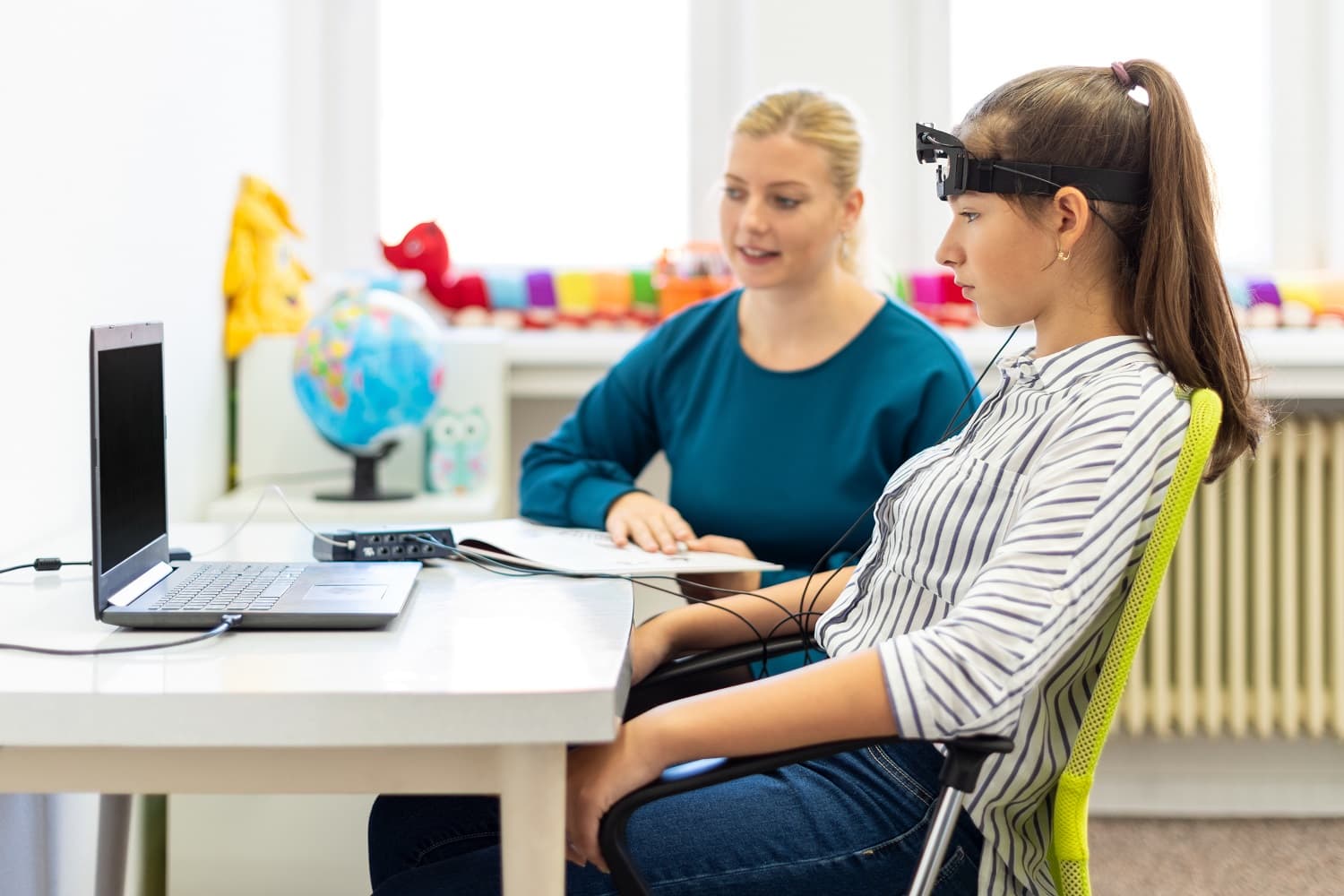

How Does Neurofeedback Work?
During a neurofeedback therapy session, the patient wears special headphones and listens to the music of their liking. Sensors are used to measure brainwave activity with the aim of detecting any electromagnetic "turbulence". When this "turbulent" processing occurs, the music that the patient is listening to will stop and the brain learns to auto-correct its processing function in an effort to maintain the music's continuity. Aside from listening to music, there are other ways of receiving this feedback such as playing a game or watching a video.
Neurofeedback sessions use the Alpha, Beta, Delta, Theta, and sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) brainwaves in retraining the brain's ability to operate at its most efficient levels.
Neurofeedback therapy is not considered a cure for disorders but rather a method of regulating or managing the workings of the brain to function in a healthier manner. This is then achieved by undergoing repeated training sessions using a computerized neurofeedback program that teaches the central nervous system to reorganize and regulate the brainwave frequencies.
Neurofeedback therapy helps in assessing the brain and provides relevant information about the areas of dysfunction that are causing symptoms so that they can be directly treated. Various neurofeedback therapy methods and equipment are used for different types of neurological problems. Some specialists use electrodes instead of headphones to measure the client's brainwaves.
What are the Benefits of Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback therapy is life-changing as it enables the client to change how their brain works so that their mind and body can function properly. It provides feedback in real time, allowing the brain to change instantaneously. Neurofeedback can be used on its own or in conjunction with other forms of therapy to address a wide range of conditions, including:
- Seizures
- Behavioural disorders
- Attention deficit disorder/attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADD or ADHD)
- Autism
- Ongoing developmental delays
- Acquired brain injuries
- Birth trauma
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Stress-related problems
- Insomnia
- Interrupted sleep patterns
- Age-related cognitive loss
- Headaches and migraines
- Respiratory problems
- Chronic pain
What Can You Expect From Neurofeedback?
Through practice and follow-up treatment sessions, neurofeedback therapy can improve the brain and alleviate the symptoms of different mental conditions. The 30-minute treatment session doesn't involve any medications or invasive procedures, just a computer and a pair of headphones or electrodes to measure the brainwave activity.
The practitioner will refer to the frequencies of the client's brainwaves, which appear on the computer screen in real time, to determine the kind of treatment that the latter needs. Some people may need to slow down their brainwaves to improve their focus, behaviour or performance, while others may need to accelerate their brainwaves.
The frequency of neurofeedback therapy varies from person to person. Some may need 10 sessions, while others may need 20 to 30. People with severe conditions are advised to undergo treatment twice or three times a week.
Is Neurofeedback Safe?
Each person reacts differently to neurofeedback therapy, but the good news is that there have been no reports of severe adverse reactions linked to this modality. If a negative reaction is experienced, the client should inform their therapist immediately so that they can make the necessary adjustments to the treatment method.